
- LEGO DIGITAL DESIGNER VIDEO ISSUE MOVIE
- LEGO DIGITAL DESIGNER VIDEO ISSUE UPGRADE
- LEGO DIGITAL DESIGNER VIDEO ISSUE SOFTWARE
Powered by LEGO Digital Designer, LEGO Factory allowed anyone to design a 3D model with digital bricks, and then order the model and have it shipped to their home. On August 29, 2005, the LEGO Group announced that, in celebration of the 50th anniversary of its System in Play, it was launching LEGO Factory. By September 2004, LEGO Digital Designer had been downloaded more than a million times.
LEGO DIGITAL DESIGNER VIDEO ISSUE UPGRADE
Over the following year, the Qube team continued to upgrade and iterate on the program, adding things like online support for creation sharing. The original LEGO Digital Designer hit the LEGO website in July 2003 as a standalone downloadable program that felt more like an experiment than fully backed piece of official LEGO Group software.
LEGO DIGITAL DESIGNER VIDEO ISSUE SOFTWARE
The following year, as the LEGO Group struggled with flattening sales and rising operating costs, SPU Darwin was shut down.Įventually, that project was handed over to another developer – Qube Software – which turned the game into a tool. The first product to come out of that idea was LEGO Creator, a sandbox-building game developed by Superscape and launched on Nov. Specifically, LMI executive producer Rob Smith said he and a team working on video game concepts for the LEGO Group decided to take their own stab at digitizing the LEGO brick in 1996. While SPU Darwin was struggling to meet expectations, another division within the LEGO Group – LEGO Media International – started playing around with another take on the digital brick. Creating just two to three digital bricks could take an entire day. But the division simply couldn’t digitize the company’s bricks at a reasonable speed.
LEGO DIGITAL DESIGNER VIDEO ISSUE MOVIE
That nearly four-minute video – actually titled The LEGO Movie – became a pitch to the LEGO Group for a research project aimed at digitizing the brick and bringing it to games, movies, and future technology that could blend the digital and physical.ĭandi, as he was known to his friends, got the ball rolling in 1993, won over the LEGO Group in 1995, and helped launch Strategic Product Unit Darwin in 1996.Īmong SPU Darwin’s four divisions was the 元D group, which focused on building a database of LEGO bricks.
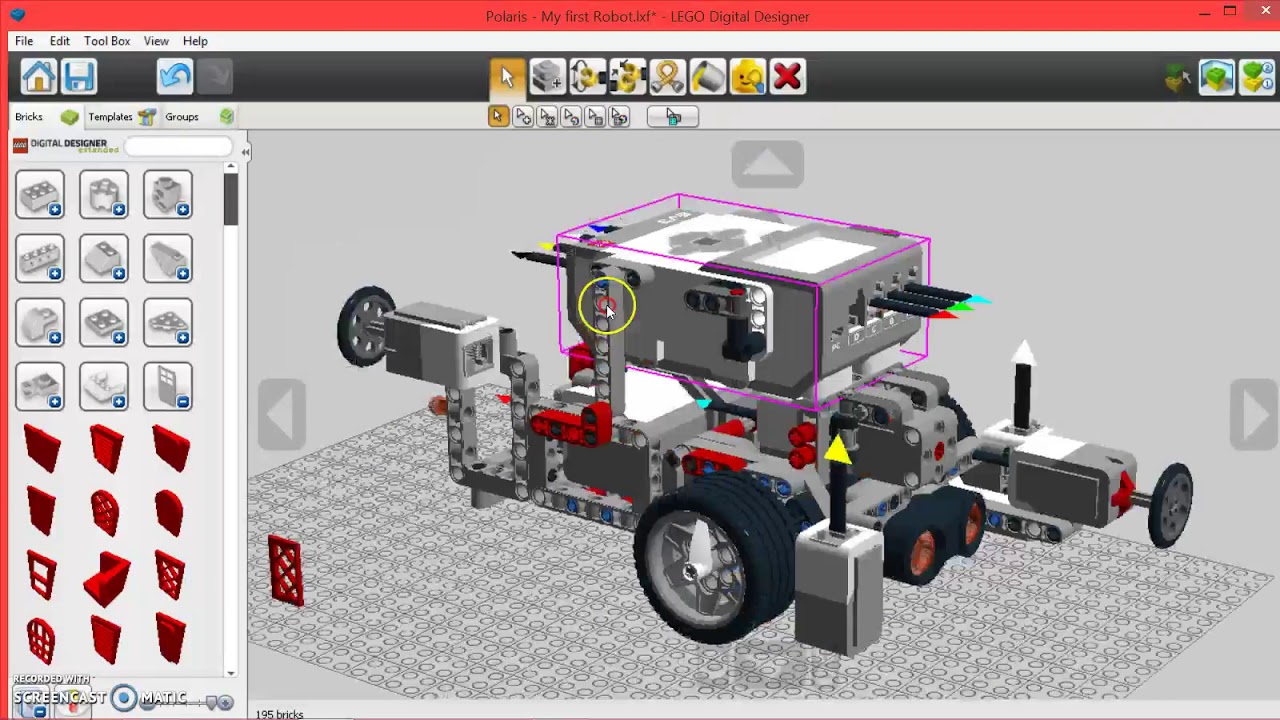


That concept of the digital brick started in Switzerland when a man who went by the name of Dent-De-Lion Du Midi convinced a group of friends to band together and work on a proof-of-concept video that would show what a digital LEGO brick would look like and how it would behave on-screen. With the digital brick, there would be no limits to what a person could build, be it a LEGO brick model, a movie or television show created entirely of bricks or even video games that breathe life into the toy. Why the LEGO Group decided to publicly retire its popular internal creation – now used in the creation of everything from LEGO brick sets to video games and movies – and instead rely on something built on a foundation of fan creation is a tale of two journeys going back decades.Ī key transformative moment in the life of the LEGO brick came in the early ‘90s when fans began to imagine what it would be like to create digital representations of the LEGO bricks and elements. The LEGO Group announced in January that it was officially retiring its long-lived LEGO® Digital Designer for fans, replacing it with the fan-empowered digital LEGO brick designer BrickLink Studio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
